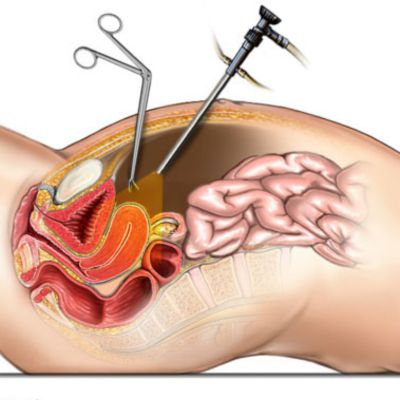
In Vitro Fertilization(IVF)
This treatment effectively bypasses the fallopian tubes and is the most effective treatment for patients with absent, blocked, or damaged tubes. The woman is given fertility drugs to stimulate her ovaries to produce many follicles Each follicle should contain one egg The chances of pregnancy are increased if more than one egg is obtained and fertilized. The number and size of the developing follicles in the ovaries are measured by ultrasound scans.
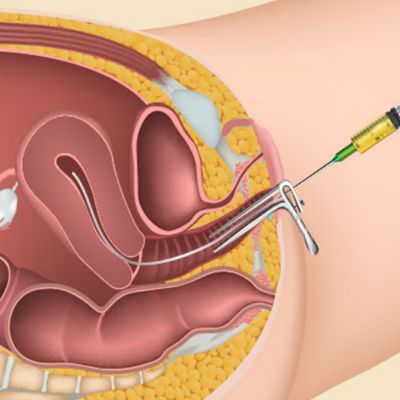
The ultrasound scans are performed at intervals during the treatment cycle. When the follicles reach the optimal size, preparations will be made for egg collection An oestradiol assay will also be carried out prior to administering HCG, to help determine the timing of egg collection. The final preparation for egg collection involves a hormonal injection given to the woman 36–40 hours pre-operatively. This mimics the natural process that normally triggers ovulation. The eggs are collected vaginally using ultrasound guidance, under general or local anesthesia.
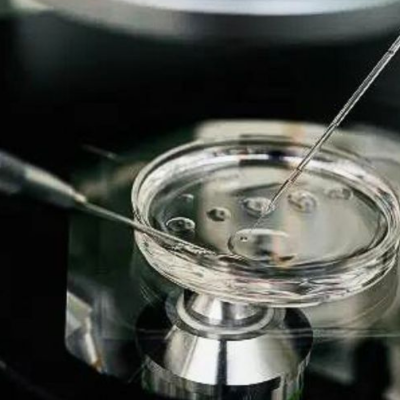
The ultrasound probe is introduced into the vagina, the ovaries are visualized and then the aspiration needle (attached to the probe) is passed through the top of the vagina into the follicles. The fluid within the follicles is aspirated and then examined in our IVF laboratory for the eggs to be identified.
After egg collection, the eggs are incubated for a short time and the sperm is then added to the eggs and incubated in the laboratory for a further 24-48 hours Providing that the semen is normal, fertilization should take place. The first signs of fertilization are shown by the presence of the pronuclei within the egg If this has occurred, the zygote should then divide into two and subsequently three, four, or more cell embryos. The fertilized eggs (now called embryos) are returned to the uterus 48–72 hours after egg collection. This is an embryo transfer.
The embryo transfer procedure is one of the most important events in IVF. It is generally a painless procedure. An abdominal scan is performed to confirm the correct position of the transfer catheter within the uterine cavity prior to replacement.

-
What is IVF?
IVF means in vitro fertilization (fertilization that happens outside the body). It involves the fertilizing eggs in the lab and the transferring
the resulting embryos into the uterus.IVF is advised for couples in whom other fertility therapies have been unsuccessful or are not
possible. -
Who needs IVF?
IVF was initially developed for women with damaged tubes. Today all forms of infertility are treated with IVF when simple
treatment fails to achieve a pregnancy. -
How are the ovaries stimulated?
The ovarian stimulation is done by injections of gonadotropins. These are naturally occurring hormones extracted from human urine or are genetically prepared. (HMG, FSH, and recombinant FSH). The final maturation of the egg is achieved by HCG injection.
-
Do the injections have any side effects?
Injections used are pure hormones that act only on the follicles; they cannot act anywhere else in the body.
-
How is egg growth monitored during Ovarian stimulation?
Ovarian stimulation is monitored by measuring the size of the follicle (the structure that contains the egg) by sonography.
Monitoring may also include blood tests for estradiol (estrogen), progesterone, and LH.
Monitoring allows the doctor to change the dose of the injections if required and also decide the date of egg collection. -
How are the eggs retrieved?
Egg retrieval or Ovum Pick up is a procedure done under short general anesthesia. A thin needle is inserted into the ovary under
ultrasound guidance and the follicular fluid is aspirated, this fluid contains the egg which is then separated in the laboratory. This
procedure is commonly also called egg pick-up. -
Will my husband be required on the day of IVF?
Your husband will be asked to produce a semen sample on the day of egg retrieval.
Abstinence for three to four days is recommended before the egg retrieval day.
The semen is processed to separate motile sperm in the laboratory. These are used to inseminate the eggs.
Please read the Semen collection instructions before collecting the sample.
(In case of difficulties, kindly revert to the hospital staff.) -
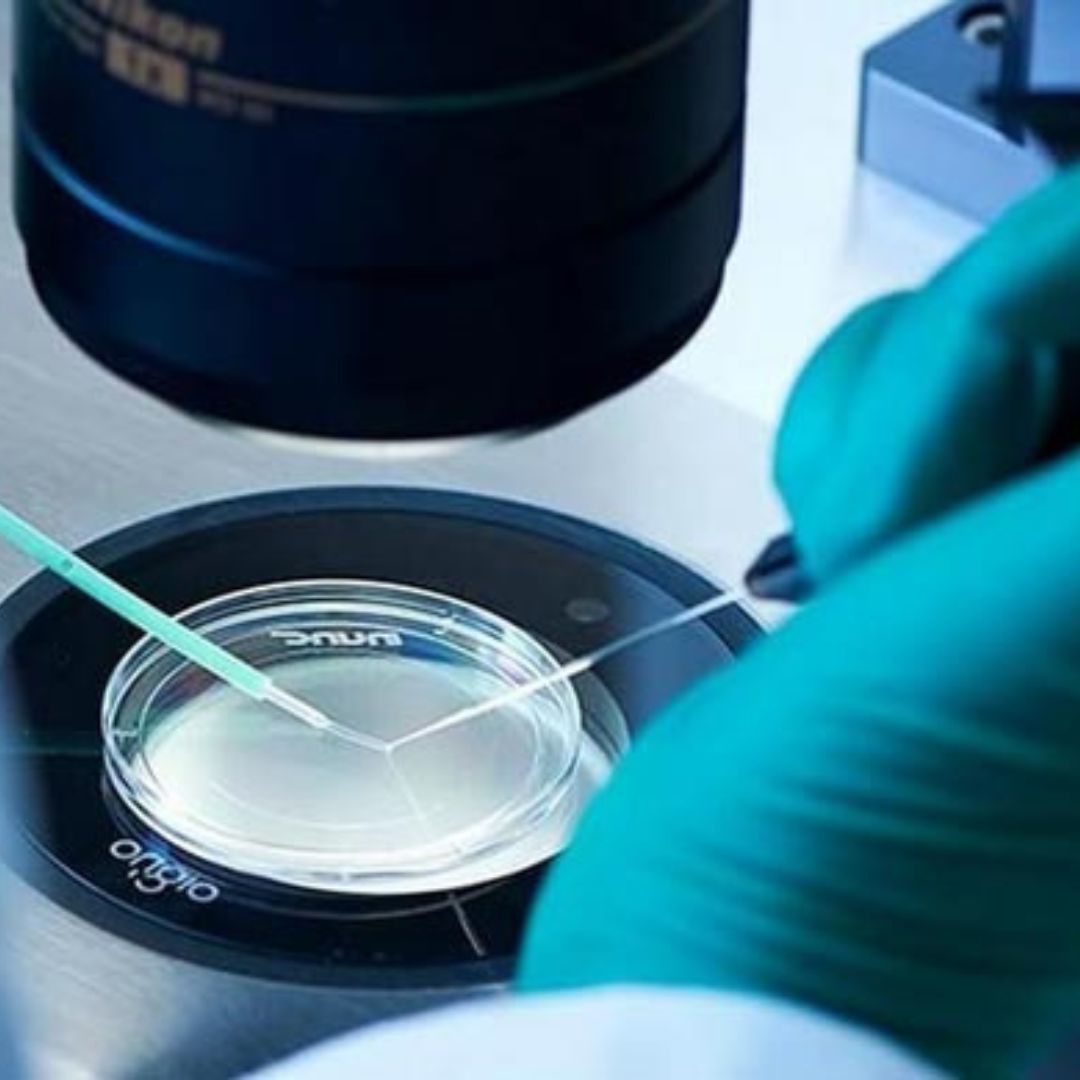
What happens in the IVF lab?
Sperms are mixed with the eggs at an appropriate time. The next day, the eggs are checked for signs of fertilization. On the 2nd and 3rd days, the embryos are evaluated under a high-power microscope.
-
How is embryo transfer done?
Embryo transfer is a painless procedure, and no anesthesia is required. Embryos are loaded into a thin, soft plastic catheter (tube). This catheter is threaded gently into the uterus. This process is performed under sonography control.
-
How many embryos can be transferred?
In our clinic, we limit the number of embryos transferred to a maximum of two. In exceptional situations, three embryos will be replaced
after discussion with both of you. -
Will transferring more than two embryos increase my chance of success?
Transferring more embryos increases the risk of a multiple pregnancy, even though it may increase the chances of getting pregnant
-
Do I need bed rest after the IVF procedure?
You can rest for an hour after the embryos are transferred, after which you can resume your normal activity.