Egg Freezing
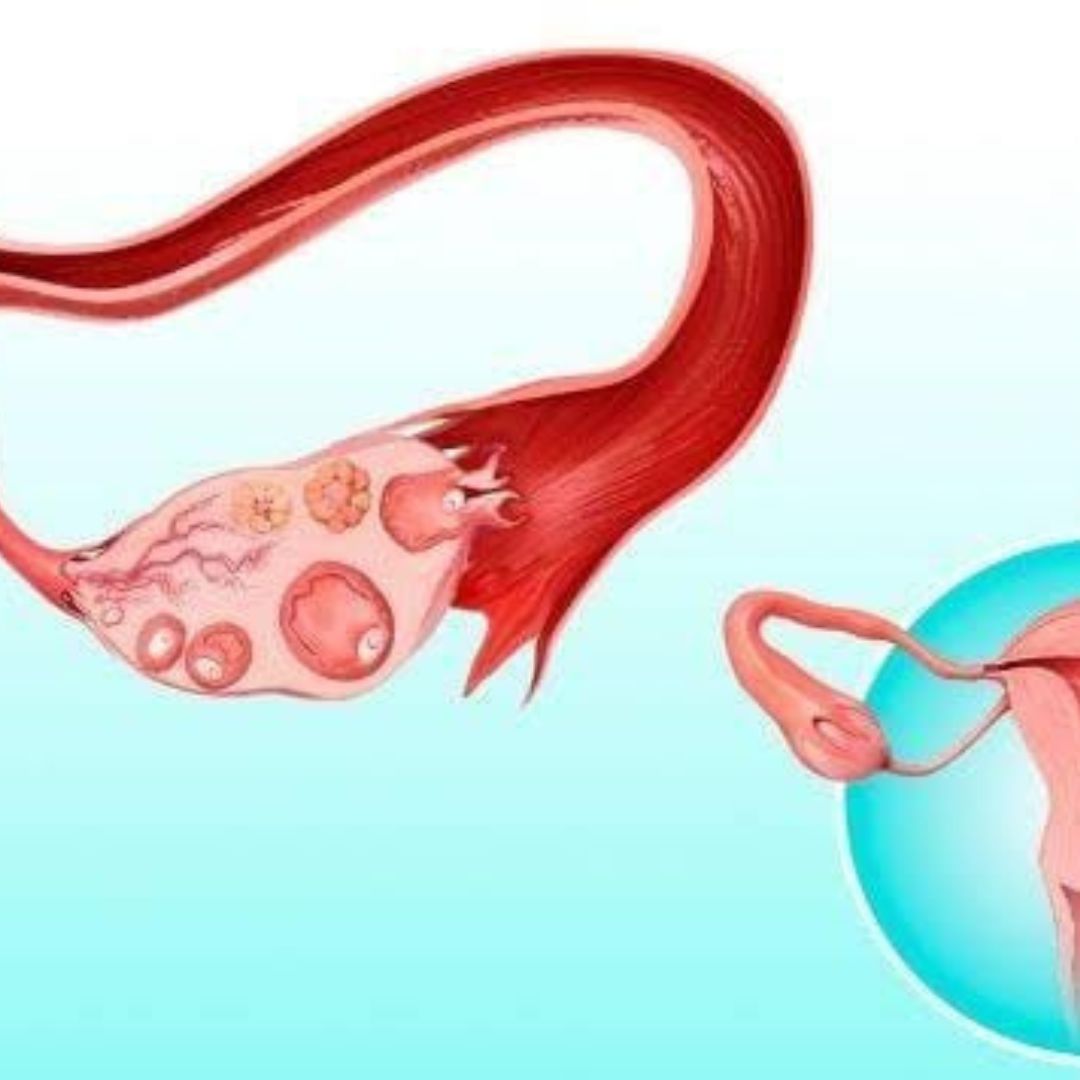
Egg freezing is one way of preserving a woman’s fertility so she can try to have a family in the future. It involves collecting a woman’s eggs, freezing them, and then thawing them later on so they can be used in fertility treatment. A woman’s chances of conceiving naturally fall as she gets older because the quality and number of her eggs drop. Egg freezing can be an attempt to preserve fertility by freezing the eggs when the woman is young and the eggs are of the highest quality.
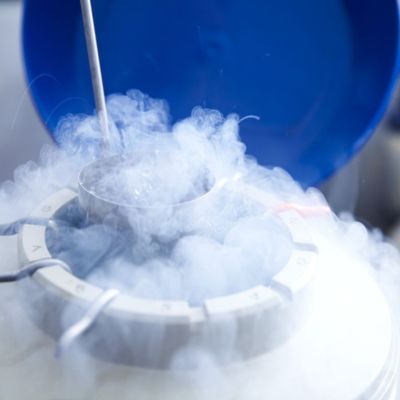
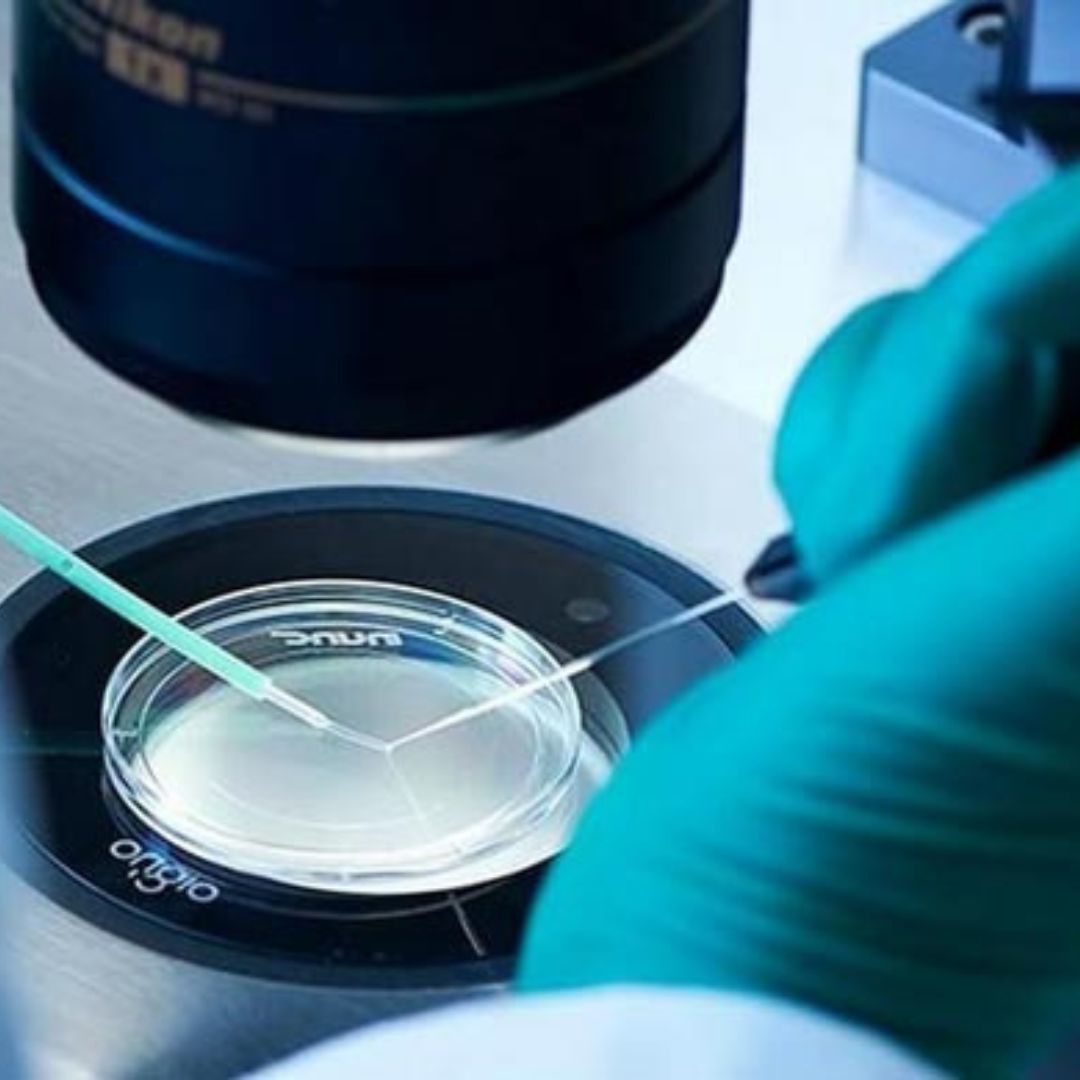
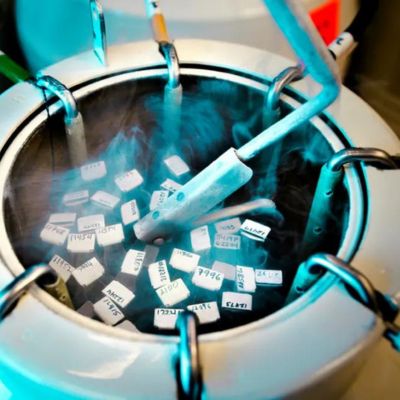
At this point, instead of mixing the eggs with sperm (as in conventional IVF) a cryoprotectant (freezing solution) will be added to protect the eggs. The eggs will then be frozen either by cooling them slowly or by vitrification (fast freezing) and stored in tanks of liquid nitrogen. Latest statistics show that vitrification is more successful than the slow cooling method. Most patients under 38 years of age will have around 7-14 eggs collected, although this isn’t always possible for patients with low ovarian reserves (low numbers of eggs). When you want to use them, the eggs will be thawed and those that have survived intact will be injected with your partner’s or donor’s sperm.